The correct solution to structural problems or planned changes to existing building structures begins with a building safety inspection and diagnosis. A structural inspection is the collection of sufficient information about the building structure. The process begins with a comprehensive inspection by a structural engineer, familiarization with the available construction documentation and identification of elements for additional inspection and diagnosis. Based on the information collected, the structural engineer prepares an analysis of the building condition in the form of a structural statement or passport. These construction documents serve as the basis for the future structural design for strengthening, reconstruction, upgrading or change of purpose. The ultimate goal is to achieve the necessary safety, extend the service life of the structure or modernization in an optimal way for the client.

In general, a structural survey can be divided into five main stages:
1. Analysis of the available construction and structural documentation and construction papers

The construction documentation for the building is a starting point for determining the quality of the project and the safety of the supporting structure. After analyzing the available documentation, it is necessary to check the correspondence between the project and the actual implementation. A common phenomenon in Bulgarian construction practice are significant deviations during implementation.
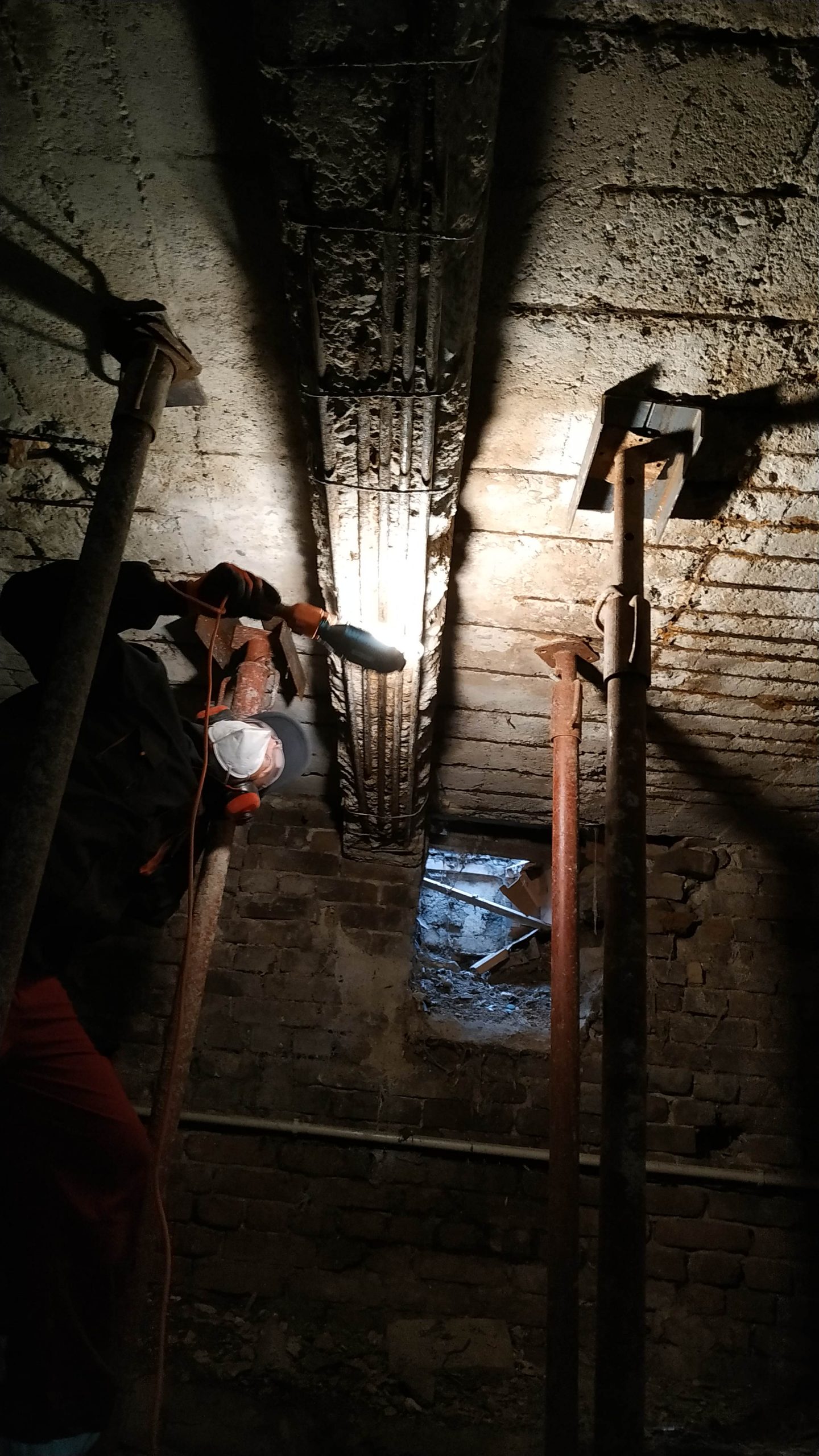
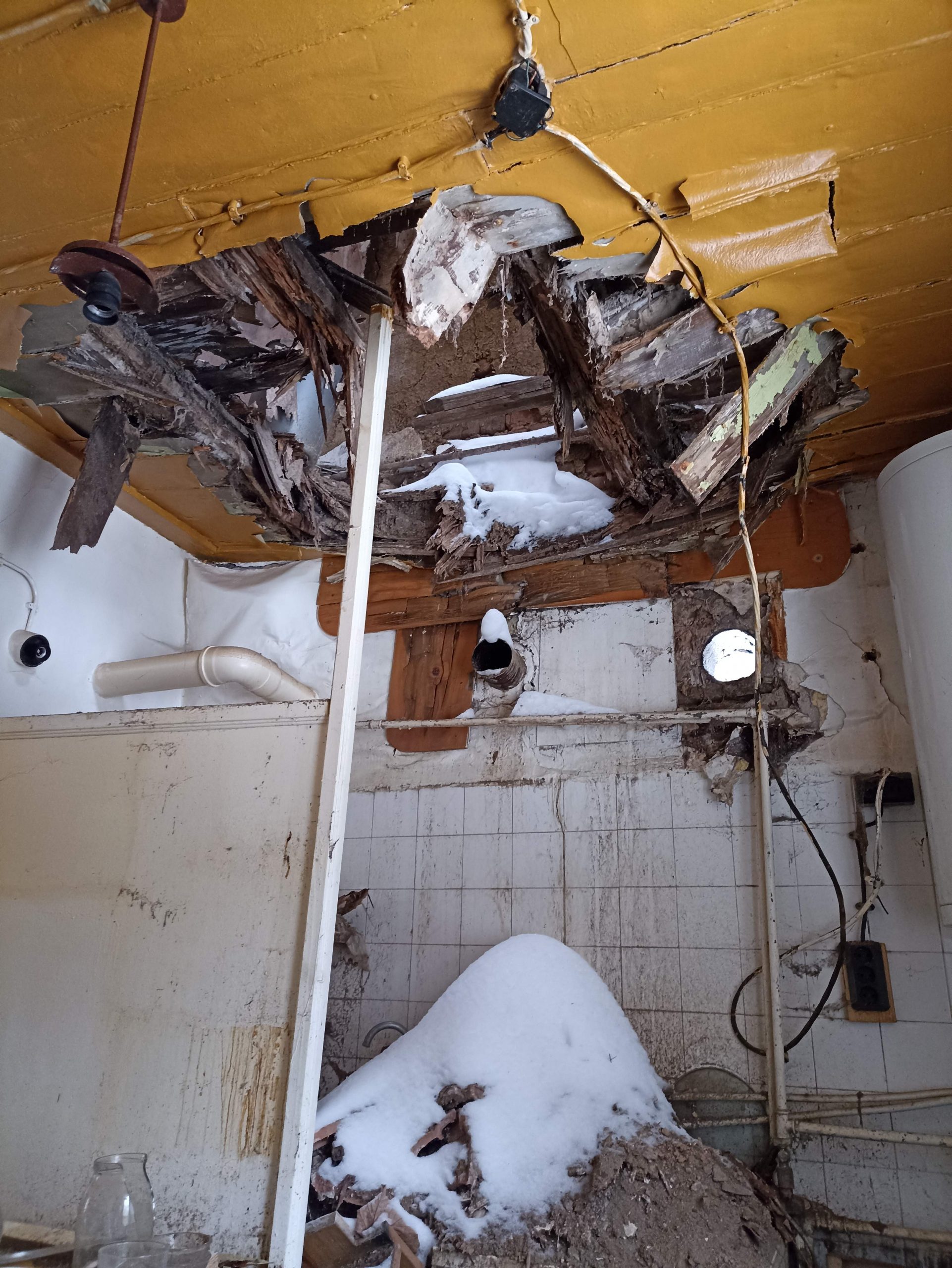
2. Diagnostics and certification of the current technical condition of the structure

3. Study of the actual and projected loads acting on the building

4. Experimental study
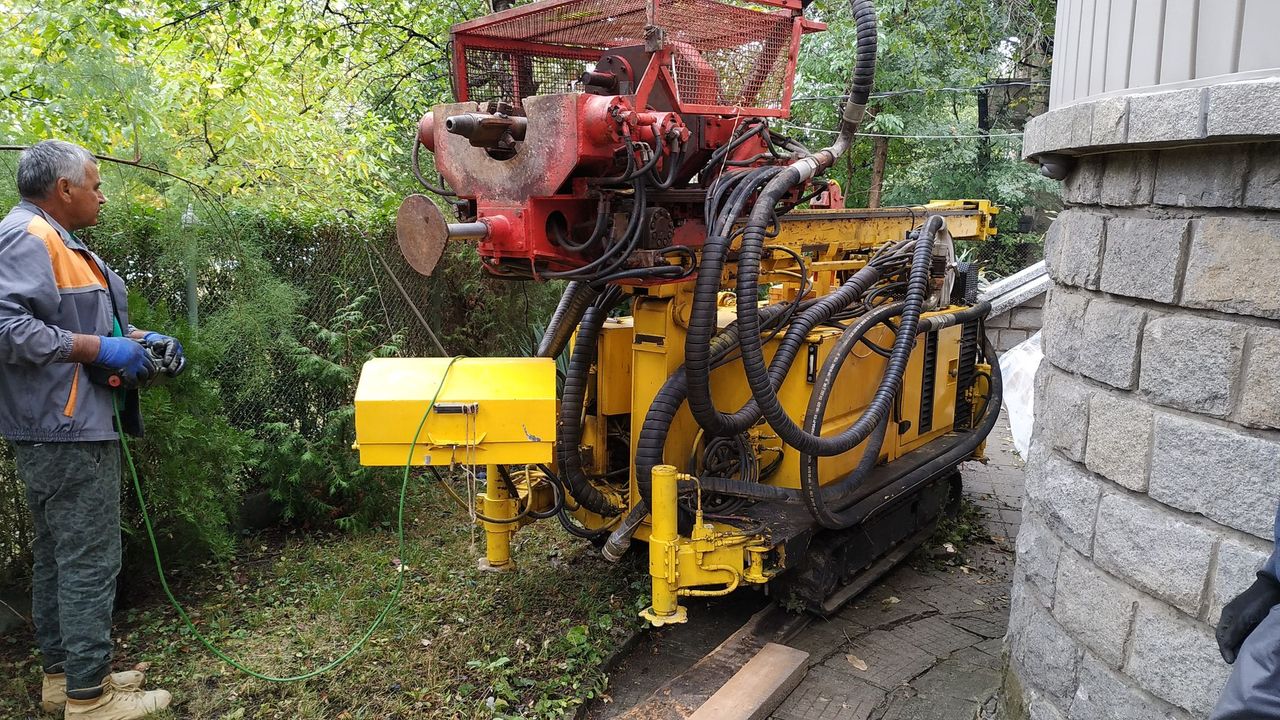
5. Geological survey of the soil under the building

6. Determination of potential reserves in the load-bearing capacity of the structure and determination of structural elements, parts and joints that need to be restored, replaced or strengthened
The initial data from the technical condition diagnostics and geological survey serve for further actions. The data from them are the basis of the restoration, reinforcement or reconstruction project. Given the dangers, complexity and complexity of the engineering task, the initial data from the survey are of particular importance and should be given special attention.

Constructive opinions
When do you need constructive feedback?
The structural statement is a necessary technical document before a renovation involving a structural or non-structural change in the building. Such renovations include those that involve the removal or construction of partition walls, the creation of openings in walls and slabs, etc. The preparation of a technical statement is also mandatory if you wish to obtain a certificate of tolerance for an existing building. A change in the purpose of a site is also accompanied by this document.
For constructions under Art. 147, para. 1, 3, 5, 7 and 12 of the ZTA, for which approval of an investment project is not required, but a construction permit is required, such as:
-outbuildings;
-greenhouses with an area of up to 200 sq.m.;
-swimming pools with a volume of up to 100 cubic meters;
-retaining walls with a height of up to 2 m.;
-fences;
-glazing of balconies and loggias;
-when legalizing existing buildings and preparing a technical passport.

What is constructive feedback?
This is a text that describes the structure in which the specified construction activities are carried out. If necessary, the statement may include calculations regarding the load-bearing capacity of the structure and the planned changes. A mandatory element is a graphic part with details for implementation.


How much does it cost to prepare a structural opinion for a building?
The price for the survey and preparation of a technical opinion varies depending on the specifics of the site. The minimum price for a technical opinion is 350 BGN.

Technical passport of a building

What does a building passport contain?
In general, the documents included in the passport provide clarity about the condition and reliability of the structure and the necessary measures for its maintenance and trouble-free operation in the future. The first chapter of the passport contains basic characteristics of the object such as identification data and parameters - type of construction, purpose, construction category, year of construction, structural system, data on past reconstructions, available documentation, etc. The second chapter includes basic volume-planning and functional indicators, part of the structures, as well as installation and technological provision. At this stage of the passportization, an architectural survey of the building may be required - in plan and facades. The conclusion is the last chapter of the passport, and it describes in detail all measures for maintaining the building in good condition and deadlines for carrying out the necessary repairs.
